Compared to the revolutionary changes in the capabilities of desktop platforms that were provided by the release of Intel 915/925 Express chipsets, the emergence of the company's new line of i945/955 Express chipsets (as well as a slightly modified version the last one - i975X) looks very modest. Small improvements affected, in fact, only support for b O higher interface speeds, the main task of the new products is to provide the basis for the newly announced dual-core Intel processors and ATI CrossFire technology. This material contains only information about the functionality of the i945/955/975, and the performance tests, in which the i925X and i955X present their generations of chipsets, are included in , since the testing was completed later.
Intel 955X/945P/945G Express
Like the first generation of the Intel Express chipset series, new line is represented by three products: top-end (i955X - without integrated graphics, with reduced capabilities for supporting older solutions, with several features characteristic of high-performance systems), integrated (i945G) and basic (i945P). Let's start in order of seniority:

- Northbridge 955X:
- processor support Intel Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, Pentium D and Pentium Extreme Edition with system bus frequency 800/1066 MHz;
- DMI bus (with ~2 GB/s bandwidth) to the ICH7/R southbridge;
- Southbridge ICH7/R:
- up to 4 (for ICH7)/6 (for ICH7R) PCIEx1 ports;
- up to 6 PCI slots;
- up to 2 devices (1 channel) ATA100;
- up to 4 Serial ATA ports for 4 SATA300 devices (SATA II, second generation of the standard), with support for AHCI and functions like NCQ;
- the ability to organize a RAID array of levels 0, 1, 0+1 (10) and 5 from SATA drives;
- up to 8 USB devices 2.0;
- High Definition Audio (7.1) or AC"97-audio (7.1) and MC"97-modem;
- special interface for connecting a proprietary 100-Mbit network controller Intel series 82562;
- harness for low-speed and outdated peripherals, etc.
Since the south bridges are common for the entire family, we will limit ourselves to the functionality of the north bridge of the i945G and i945P:

- Northbridge 945G:
- PCIEx16 graphic interface;
- integrated graphics core GMA 950;
- Northbridge 945P:
- support for Intel Celeron D, Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, Pentium D and Pentium Extreme Edition processors with a system bus frequency of 533/800/1066 MHz*;
- dual-channel DDR2-400/533/667 memory controller supporting up to 4 non-ECC DIMMs with a total capacity of up to 4 GB;
- PCIEx16 graphical interface.
* UPDATE: shortly after the release of processors based on the Core 2 core, the information on the manufacturer's website (Intel) was updated, and the i945P/G chipsets received official support retroactively Core processors 2 Duo (which de facto also means support for Core 2 Extreme/Quad and Celeron on the Core 2 core).
Now briefly on the characteristics, as well as the differences between the new chipsets and their competitors. The i955X lacks support for “low-speed” processors (with a 533 MHz bus) and memory (DDR2-400), while supporting more memory, ECC and proprietary memory acceleration technology (Memory Pipeline). i945G - the same i945P, only with integrated graphics. Compared to previous Intel chipsets, support for DDR2-667 memory has been added (whether it is needed is a separate question) and a bus frequency of 1066 MHz (however, it already appeared in the i925XE).
None of this family of chipsets has the ability to “split” the graphical interface into 2 PCI Express ports, but the operation of two video cards in a pair (NVIDIA SLI/ATI CrossFire) is still possible. To do this, a PCIEx4 port is organized using the peripheral PCI Express ports of the south bridge, to which the second PCIEx16 form factor slot on the motherboard is connected. However, NVIDIA does not allow SLI to be implemented on chipsets from other manufacturers, so, barring the case of driver hacking, Intel chipsets are limited to a couple of ATI video cards. But CrossFire is officially allowed only on the i955X (of course, purely for marketing reasons), and mid-level chipsets for this technology are only “suitable” for ATI's own production.
The new line of south bridges is represented by only two models (last year’s experiment with support wireless network failed). ICH7 differs from ICH6 only in b O Higher speed of the Serial ATA interface - now 300 MB/s, as in the SATA-II standard, but without AHCI. The ICH7R version adds RAID support for SATA hard drives, and compared to the ICH6R, this support is expanded: now, in addition to RAID 0 and RAID 1, levels 0+1 (10) and 5 are available. In addition, the ICH7R version is given 2 extra PCIEx1 ports, which may be useful considering the possibility of using 4 main ones for the PCIEx4 slot (which can be useful for combining two PCIE video cards in SLI).
Compared to competitors' solutions, the most interesting of which is NVIDIA nForce4 SLI Intel Edition, the i945/955 is inferior in the number of supported ATA devices (and this is still important for many), USB ports and has a less successful SLI mode organization scheme. Pros: HDA support, integrated graphics for i945G, more interesting RAID modes(with less flexibility in choosing devices to combine into a RAID array).
Intel 975X Express
At the end of 2005, Intel announced a new chipset, which can only be described as the i955X version. In fact, absolutely all characteristics of the i975X, except one, coincide with those of its predecessor:

- Northbridge 975X:
- support for Intel Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, Pentium D, Pentium Extreme Edition, Core 2 Duo and Core 2 Extreme processors with a system bus frequency of 800/1066 MHz;
- dual-channel DDR2-533/667 memory controller with support for up to 4 DIMM modules with a total capacity of up to 8 GB (modules with and without ECC can be used);
- PCIEx16 graphic interface or 2 PCIEx8 graphic interfaces.
Moreover, in the only point that does not coincide, the i975X does not cancel, but expands the capabilities of the i955X: the new chipset allows you to create 2 graphics ports by “splitting” the original PCIEx16 graphic interface into two x8 ones. Of course, this is needed, first and only, for faster CrossFire operation (well, there are still more free PCI Express ports in the south bridge). Otherwise, including the same supported south bridge models - ICH7/R, the chipsets are the same.
However, it is worth noting that, due to the difference in release dates, the i975X supports new generation processors Intel Core 2 Duo/Extreme. From Samog O
Nothing depends on the chipset here, but official support for Core 2 is granted by marketers to only one top solution, just as the first quad-core processors should officially work only in motherboards based on the i975X. Motherboards on i955X are incompatible with processors of the new microarchitecture.
Before we move on to testing the HP DV1000T, I need to introduce you to Intel's new 945PM/GM chipset technology. This will help you better appreciate some of the tests that are to come. Again let me note that we will be publishing a more detailed look at the 945GM chipset soon.
The two key aspects of Intel's Centrino Duo Mobile technology are Core Duo mobile CPUs and the 945PM Express and 945GM Express chipsets. The 945PM is used in mobile computers with discrete graphics processors - graphics processors that are external to the 945 chipset - and provides all chipset functionality but the graphics functionality provided by the discrete graphics processor itself. The 945GM, which also supports discrete processors but is not as cost effective as the 945PM if a discrete processor is used, includes an integrated graphics processor, the Intel Graphics Media Accelerator 950 (GMA 950).Aside from the graphics differences, the two chips are identical.
The following table shows the characteristics of the two chips. It is based on Intel specifications data.
| Mobile Intel 945GM Express Chipset | Mobile Intel 945PM Express Chipset | |
|---|---|---|
| Processors Supported | Intel Core Duo processor Intel Core Solo processor Intel Celeron M processor |
Intel Core Duo processor Intel Core Duo processor Low Voltage (LV) Intel Core Duo processor Ultra Low Voltage (ULV) Intel Core Solo processor Intel Core Solo processor Ultra Low Voltage (ULV) Intel Celeron M processor Intel Celeron M processor Ultra Low Voltage (ULV) |
| FSB Speed | 667 MHz 533 MHz |
667 MHz 533 MHz |
| #SO-DIMMs/Max Memory | 2 SO-DIMMs / up to 4 GB Max System Memory @ 533 MHz (use with 667 MHz memory not validated) | |
| Memory Type | DDR2 667 MHz DDR2 533 MHz |
DDR2 667 MHz DDR2 533 MHz |
| Memory Channels | Dual/Single Channel | Dual/Single Channel |
| ECC Parity | No | No |
| Integrated Graphics | Intel GMA 950 | N/A |
| Discrete Graphics | PCI Express x16 | PCI Express x16 |
| Integrated TV Out | Yes | N/A |
| Max Panel Display Resolution | LVDS: Up to UXGA (1600x1200) | N/A |
| Dual Display Options | Concurrent/Simultaneous | Concurrent/Simultaneous |
| Power Management | Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology, Deeper Sleep | |
| Intel Display Power Savings Technology | Yes | N/A |
| PCI Masters | 7 | 7 |
| IDE/ATA | ATA 100 (1 Ch.) SATA 150 (2 Ports) |
ATA 100 (1 Ch.) SATA 150 (2 Ports) |
| USB | 8 Ports USB 2.0 | 8 Ports USB 2.0 |
| Integrated LAN MAC (w/10/100 Ethernet or HTNA) | Yes | Yes |
| PCI Express I/O Ports | 4X1 PCI Express Ports | 4X1 PCI Express Ports |
| Audio Circuitry | Intel High Definition Audio 24bit 192KHz, AC"97 2.3 Audio | |
| Supported ICH | 82801GBM / 82801GHM | 82801GBM / 82801GHM |
The HP DV1000T has the 945GM Express chipset and borrows up to 128 MB of system memory for graphics processing. The N6410, with a separate ATI Mobility Radeon X1400 graphics processor (128 MB of dedicated memory and the ability to use up to 128 MB of shared systen memory) uses the 945PM Express chipset. Both graphics processors can do 2D and 3D graphics. As you will see the ATI processor is the better performer of the two.
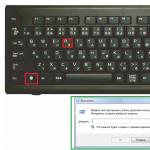
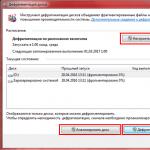
This is the interface used to modify the characteristics of the Intel GMA 950 graphics processor.
Before we leave our discussion of the 945GM/PM chipset, I need to call your attention to one of the rows in the above table, the one labeled "#SO-DIMMS/Max Memory." Check out the phrase in each column "(use with 667 MHz memory not validated)." Say what? Well at least one reason for the caveat has to do with system memory clock specs. It turns out that system memory clocks in some 945GM/PM based systems don"t or at least at one time didn"t meet DDR2 667 MHz DRAM device jitter requirements. This can cause problems with DDR2 667 MHz memory timing, if the memory doesn't meet all of the other requirements for DDR2 DRAM from Intel and JEDEC, the semiconductor engineering standardization body of the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA). Intel claims that no functional memory failures have been observed.
Specifications:
The difference between the i946GZ and G965 lies in the latter’s support for DDR2-800 memory, the possibility of being equipped with a new south bridge ICH8 (not ICH7) with a corresponding difference in the sets of integrated controllers and technologies, as well as the presence of a different graphics core - GMA X3000 (support for ClearVideo technology) and technology working with Intel Fast Memory Access memory.
i946PL
Difference from i946GZ: lack of an integrated graphics core. Otherwise, all possibilities are similar.
Intel has introduced budget modifications to the i945 chipset, which supports dual-core Pentium D processors.
Discrete 945PL It features support for processors with FSB 800/533 MHz, has a dual-channel DDR2-533/DDR-400 memory controller and a PCI-Express x16 graphics port.
Integrated 945GZ contains the Intel GMA 950 graphics core, supports processors with FSB 800/533 MHz, is equipped with a single-channel DDR2-533/DDR-400 memory controller, and does not have a PCI-Express x16 port.
The 945/955 series is built on a two-chip design: the chipset consists of two controllers - system (MCH) And peripheral (ICH) , connected via a dedicated high-speed bus. This approach provides flexibility when building motherboards. The 945 series chipsets use exactly the same bus (DMI - 2 Gbps) as the 915/925 chipsets; board manufacturers can create various combinations of MCH and ICH bridges.
945/955 chipsets support dual-core Intel processors. Previous chipsets are not compatible with them. The 945/955 chipsets officially support the 1066 MHz bus.
MCH North Bridge.
Memory controller practically unchanged compared to the 915/925 chipsets, but Intel completely abandons DDR support and adds a frequency of 667 MHz. As before, the memory controller supports two different mode operation of two memory channels – alternation, when addresses are distributed in turn between both channels in 64-byte increments, and asymmetric mode, when addressing the second channel begins immediately after the first. The first mode provides speed and simultaneous access to both channels, the second provides complete flexibility. Now it is no longer necessary to fill both channels with the same modules - it is enough that the memory capacity in both channels is the same (this rule must be observed only for the interleaved mode).
South Bridge ICH.
Received serial number “7”, supports interface for hard drives Serial ATA with a throughput of 3 Gbit/s (300 Mb/s).
Support RAID and all the features of Serial ATA (interface ACHI) is implemented only in ICH7R - a special version of the south bridge, which will be installed only on expensive motherboards. Level 10 (combination of 0 and 1) and Level 5 (storing information for checking and restoring integrity on a separate disk) modes have been added to the list of RAID versions. Two ports have also been added to the ICH7R PCI Express x1– now there are 6 of them.
Built-in network controller does not support gigabit networks, built-in wireless network or FireWire never appeared, compatibility with older codecs remains AC'97 along with HD Audio.

Integrated Graphics
The integrated Intel GMA950 (945G) graphics has virtually no changes compared to the GMA900, the previous generation graphics. There is no hardware processing unit for vertex shaders and even T&L geometry, but there are 4 rendering pipelines and support for pixel shaders version 2.0, plus more clock frequency– from 333 to 400 MHz, further optimization of the graphics core was carried out.
As before, when installing an external video card into the PCI Express slot, the integrated graphics are disabled. Their simultaneous operation is impossible. However, using a special ADD2 module, you can expand the capabilities of the integrated graphics - add TV outputs and a digital DVI output. At the same time, it is possible to operate two independent screens, and now (a feature of the 945G) the “Dual Display Zoom” mode has been added - enlarging part of one screen on the other.
The 945 series includes: 945P without integrated graphics and 945G with an integrated video core.
Chipset characteristics (in comparison with 955 are as follows):
Characteristic | |||||
Memory channels | 2, dual channel mode |
||||
Memory type | DDR2, 667/533/400 |
||||
Slots/volume | |||||
ECC control | |||||
| No | |||||
| Flex Memory | |||||
| Graphics | No | Intel GMA 950 | No | ||
| PCI-E x16 | 1 | ||||
| PCI-E x1 | |||||
| Drives | SATA II 4 ports, EIDE 1 port |
||||
| Matrix Storage | NCQ, RAID 0, 1, 5, 10 | ||||
| Scheme | 82955X | 82945G | 82945P | ||
| I/O hub | ICH7/ICH7R | ||||
Chipsets i945G/i945P
The integrated i945G chipset differs from the separate i945P only in the presence of graphics Intel cores Graphics Media Accelerator (GMA) 950. Otherwise, both chipsets are identical. The new south bridge (IHC7R) received two additional PCIe 1x lanes (there are now 6 of them instead of 4); introduced support for SATA II instead of SATA (4 ports); Dual-channel memory access bus increased throughput from 8.5 GB/s to 10 GB/s (FSB 1066 MHz support); Added the ability to use DDR memory, DDR2 only.
Intel 945G

Block diagram of Intel i945G chipset
Structurally, this is the same i945P, to which the GMA 950 graphics core was “glued”. Therefore, if you do not take into account the built-in video, all the characteristics of the named chipsets are absolutely identical.
| Comparative characteristics of chipsets with integrated graphics | ||||
Characteristic | Intel 945P Express | Intel 945G Express | NVIDIA GeForce 6100 + nForce 410/430 | ATI Radeon Xpress 200G |
North Bridge | ||||
Intel Celeron D, Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, Pentium D and Pentium Extreme Edition | AMD Opteron, Athlon 64 (FX/X2), Sempron |
|||
FSB, MHz | ||||
Memory controller | dual-channel DDR2-400/533/667 controller with support for up to 4 DIMM modules with a total capacity of up to 4 GB | |||
GUI | ||||
GPU frequency | ||||
Pixel pipelines | ||||
Vertex processors | ||||
DirectX support | ||||
South Bridge | ||||
PCI Express, lines | 20/22* PCI Express x1 | 20/22* PCI Express x1 | 17* PCI Express x1 | 22** PCI Express x1 |
PCI, lines | ||||
Parallel ATA, channels | ||||
SerialATA, ports | 4 x 3 Gbit/s, NCQ | 4 x 3 Gbit/s, NCQ | 2/4 x 3 Gbit/s, NCQ | 2/4 x 1.5 Gbit/s |
RAID support | 0, 1, 0+1 (10) and 5 of SATA drives | 0, 1/ 0, 1, 0+1 (10), 5 | 0, 1 of SATA drives |
|
USB 2.0, ports | ||||
Sound | Intel | High Definition Audio (7.1) or AC"97 (7.1) | High Definition Audio (7.1) or AC"97 (7.1) |
|
* 16 lanes are used by PCI Express x16 port
** 16 lanes are used by the PCI Express x16 port and 2 are used as a bus for connecting the north and south bridges.
The GMA 950 graphics core has twice the performance in 3DMark05 tests of Intel's previous integrated solution - GMA 900 (i915G). There is support for HDTV up to 1080i resolution. Looking at the table, it is quite difficult to determine which IGP is stronger - GMA 950, Radeon Xpress 200G or GeForce 6100 On the one hand, the first two have more pixel pipelines: 4 versus 2, but not a single vertex pipeline, leaving the task of calculating shaders to CPU, while NVIDIA's brainchild has one vertex unit. Radeon Xpress 200G operates at a significantly lower frequency than competing solutions. On the other hand, the number of rendering lines, as well as the core frequency, are rather controversial criteria for assessing accelerator performance in 3D applications. Especially when comparing solutions from different developers. The GMA 950 and Radeon Xpress 200G support Shader Model 2.0 in hardware, while the GeForce 6100 can handle version 3.0.
GA-8I945GMH
GIGABYTE presented the first motherboard for systems with Intel technology Viiv. The model has been certified by Intel for compatibility with the Viiv platform.
Technical characteristics of GA-8I945GMH:
- Chipset: Intel 945G Express/ICH7-DH;
- Form factor: Micro-ATX;
- Buses: PCI Express x16, PCI Express X1, two PCI;
- RAM: four slots for DDR2 667, up to 4 GB;
- Network: Intel Pro 1 Gbps;
- Interfaces: four SATA II ports, one PATA, eight USB 2.0;
- Audio codec: eight-channel Intel High Definition Audio.