Windows families, starting with the obviously raw and unfinished modifications of 95 and 98, are simply replete with the presence of system tools that are usually hidden from the eyes of the average user. In a general sense, this entire set can be called Windows Management Instrumentation, although you can also find a separate service responsible for using it in the system. Let's try to figure out what it is, what tools are included in this set, why the user needs to use them, and how to manage the system with their help.
Windows Management Instrumentation: What is it?
To begin with, let's briefly dwell on what this set is. First of all, you need to clearly understand that this is a set of tools, and not a separate program. The manual for Windows Management Instrumentation is quite clear about this. The set itself consists of many services and processes that can be used for completely different purposes, and if necessary, even troubleshoot problems that arise. The main tasks of the entire toolkit include the following:
- obtaining information about the operating system, hardware and software of the computer;
- managing system configuration and other components;
- monitoring system stability and resource loads;
- checking and diagnosing the OS and the main components of the computer;
- identification and elimination of possible malfunctions and failures.
Useful tools that every user needs to know about
It goes without saying that absolutely all the tools that are part of the Windows 10 management instrumentation and versions below cannot be considered purely physically. Therefore, we will focus only on the most basic and precisely those that the user may need most often. Among them, the most frequently used are the following sections:
- system configuration;
- computer management.;
- activity, status, performance and stability monitors;
- checking and cleaning disks or removable media;
- memory diagnostics;
- troubleshooter.
Of course, this is not a complete list of everything that could be included in the Windows Management Instrumentation, but for the average user, this set is enough for now.
Getting information about the system
Unfortunately, few users know or seriously think about the fact that almost exhaustive information about the operating system, software and hardware can be obtained using the system itself, without resorting to third-party utilities. The latter, of course, are somewhat more informative, however, many of them are paid and are used mainly for overclocking equipment, which is not recommended without special knowledge and skills.
Among the main tools of the Windows management toolkit, the msinfo32 and winver applets, called from the Run menu, can be especially distinguished. The first provides data mainly about the hardware, the second is intended to clarify the current version of the operating system.
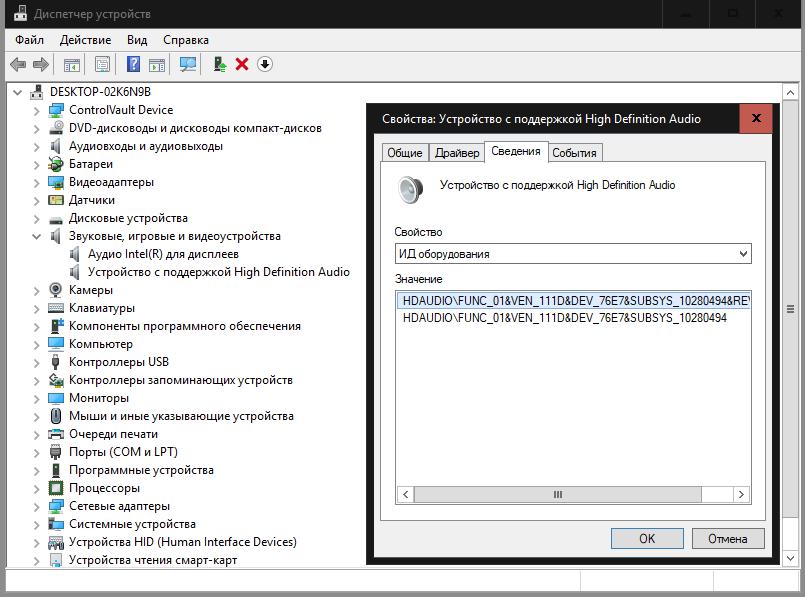
In addition, the Device Manager can be called a very powerful tool, which allows you to find out almost everything about the installed hardware and virtual equipment, manage drivers, and also fix many problems in its operation. For example, the special identifiers DEV and VEN can be used to find the most suitable control software if the system cannot find and install it on its own.
Computer system controls
The computer management section is one of the most significant. It includes several main components, of which the Task Scheduler, disk management, performance, event viewer, services, and the already mentioned Device Manager can be highlighted.
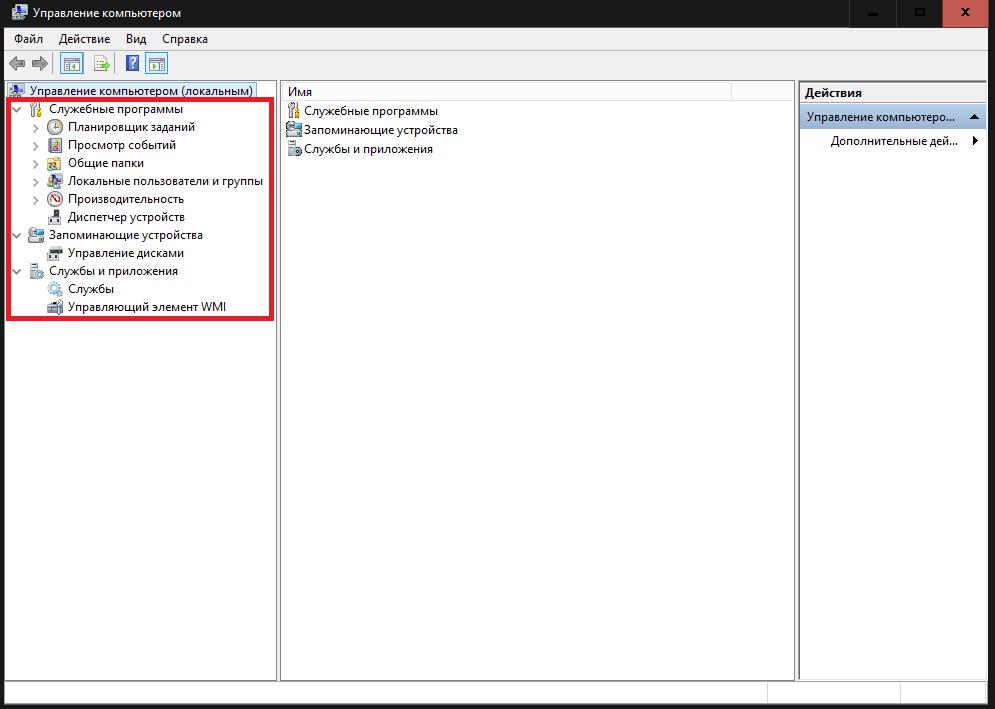
You should immediately pay attention to the fact that any of these tools can be called separately without resorting to using the main section.
As for the tools, few ordinary users fully understand the possibilities of the same scheduler. But in it you can create automatically scheduled tasks, including even turning the computer on and off. One example is the work of the KMSAuto Net application, with the help of which the operating system itself or office products were activated. Naturally, the program itself creates a new task, but if desired, the reactivation period can be changed.
Disk Management is an indispensable tool. It appeared only in the seventh version, and with its help it became possible to partition disks or perform more complex actions with them directly in a running system (previously this required third-party utilities).
The event viewer section speaks for itself. It provides information regarding all recent activities on the computer, including error reports, which can serve as a starting point in identifying and resolving critical computer failures.
The services section is used to manage all software components. It can be set to enable or disable absolutely all software processes, including those that run in the system in the background. For example, it is in this section that you can completely disable it by deactivating several components responsible for it (if anyone does not know, disabling automatic search and installation of updates in the Update Center is not enough to completely deactivate the service).
The performance utility is more related to the monitoring part, but it should not be discounted either.
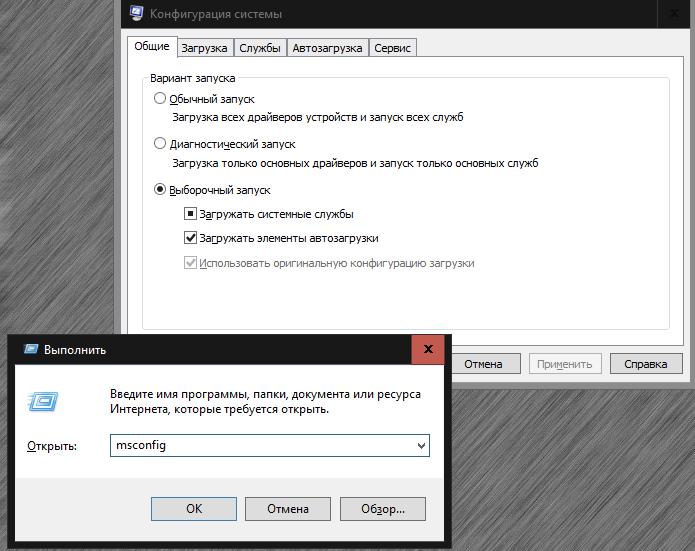
But (msconfig) is an absolutely indispensable tool, since it is here that the choice of the bootable OS at startup is set, if there are several of them, the type of start is set, some services that start with the system and startup elements are managed (in Windows 10 it is placed in the "Task Manager") etc.
Monitoring
In terms of performance, most users usually turn to the "Task Manager", in which you can monitor active or disabled processes and control their behavior. Yes, this is true, but the user will still not get a complete picture of what is happening.
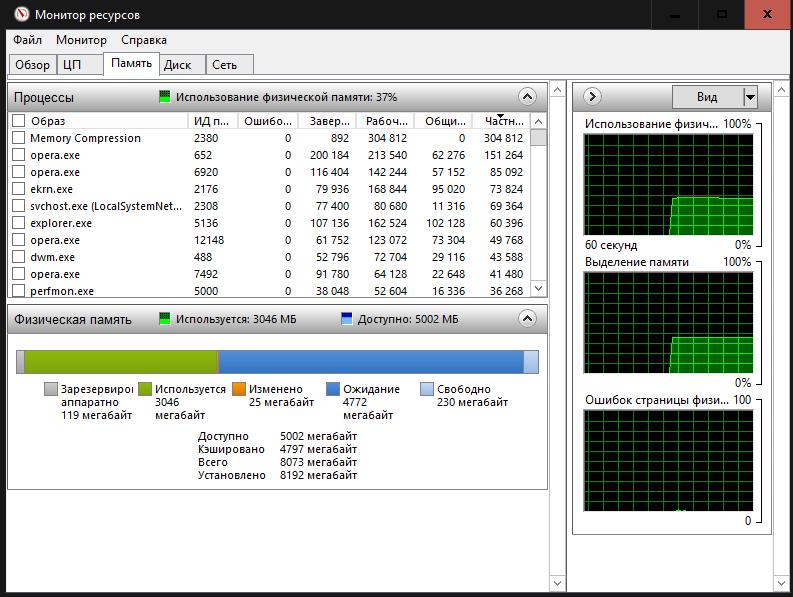
To display detailed information, it is better to use the so-called resource and system stability monitors, in which you can get maximum information about the operation of your own computer system, and, if necessary, take measures to prevent problems and failures.
Checking Components and Troubleshooting
As for the verification tools, here you can highlight actions with disks or removable media and testing RAM. However, they are not suitable for testing system components. In case of critical failures, the system can be brought to a working state only by means of the command line. For example, you can check the integrity of important files responsible for the functioning of Windows and restore them if problems are found with the sfc /scannow command. In general, in the command console, which ordinary users clearly dislike, you can perform actions that are not available through the graphical interface.
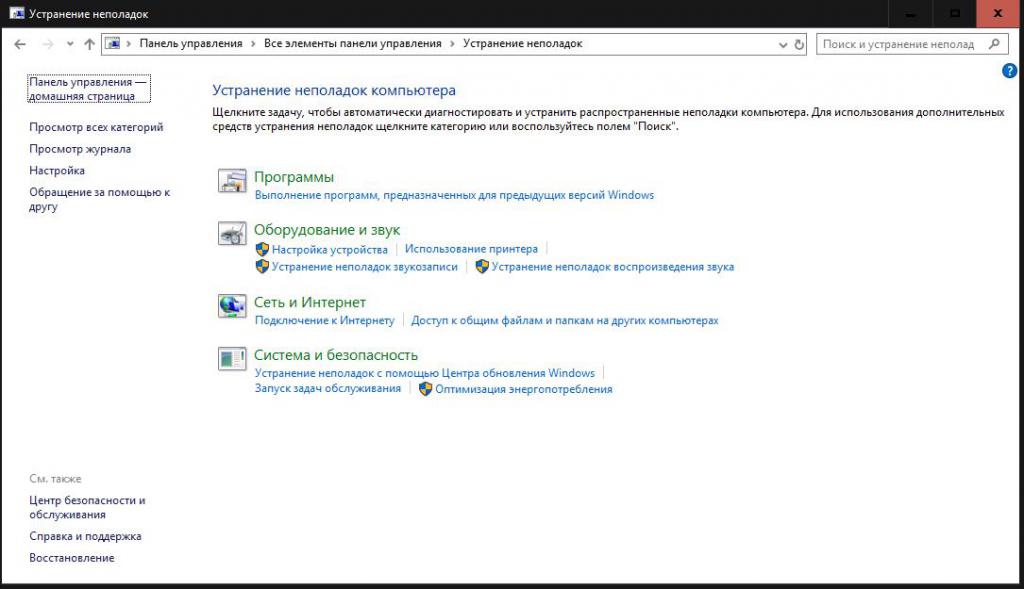
Finally, sometimes you can use an automated troubleshooter to help you identify and fix failures yourself. Sometimes it works, sometimes it doesn't. But as the first solution when errors are detected in the system or in the operation of the equipment, it is definitely worth using it.
Other Important Components
As mentioned above, in any version of Windows, you can count a lot of necessary tools. The most significant are the registry editor, as well as group and local policy tools, which, by and large, duplicate registry settings, but with a lower priority. And, if an ordinary user can make some experiments with policies, then it is strictly forbidden to interfere in the registry without a full understanding of the actions performed, since there are no means of undoing actions in the editor itself (they are provided only when changing key values). But it is with the help of the registry file to which the export was made that the operating system, with the appropriate knowledge, will not be difficult (the same applies to manually creating all kinds of backups and sample disks with a running operating system and all its contents).
How to disable Windows Management Instrumentation and is it worth it?
It remains to look at one of the most important problems. Quite often, some users notice that an active Windows Management Instrumentation process is using the processor and try to turn it off. Here you need to understand that the load on resources at such moments is not made by the main service, but by running system or user processes.
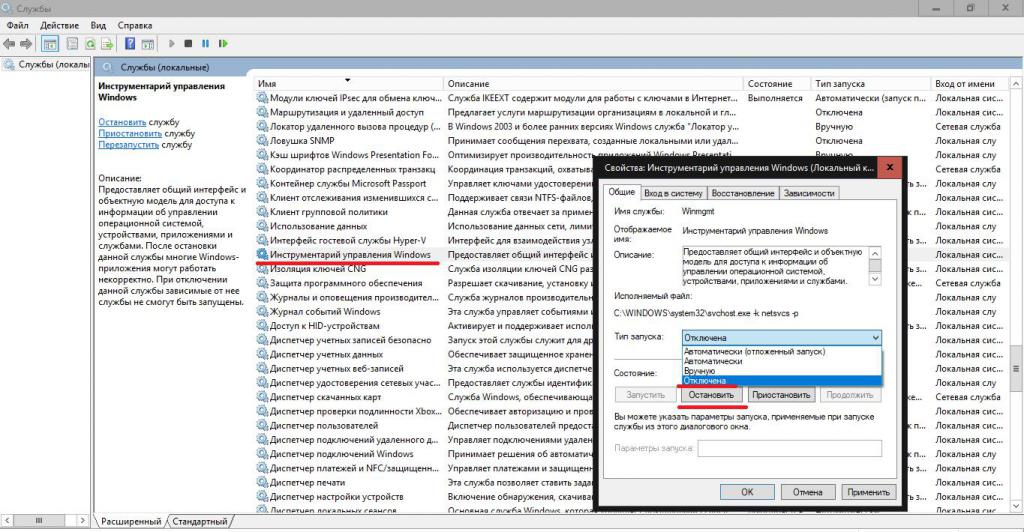
You can deactivate the toolkit in the services section, but, as it is already clear, it is not recommended to completely disable the Windows Management Instrumentation service in any case, since access to many tools will be limited or blocked, yes, and the entire system, including some programs, may be unstable .