Unfortunately, it often happens that a Windows user needs to rename or delete any files and folders, and the system suddenly starts to issue error messages 0x80070490 “Element not found” for no reason (for example, regarding certificates) , although the user is sure that this information is available. Let's figure out what to do in such a situation.
Circumstances when the error "Could not find this element. It is no longer in... (file path). Check file location"
Yes, indeed, such an error followed by a warning can occur very often. The simplest situation is too long file names inside folders, when the system writes that it is impossible to move, copy, or rename such a folder.
And it is after this that the message of interest to us appears that this element could not be found. How to remove leftovers? After all, it is clear that when copying, moving or deleting, the system nevertheless initially made such an attempt. Another thing is that it was not successful, which led to problems.
It turns out that in fact the folder or files are present on the disk, the system no longer recognizes them in the initial version. In addition, the message "Element not found" may appear when any files or folders are blocked by system processes (currently in use), say, antivirus software or the same "Explorer" (Explorer service).
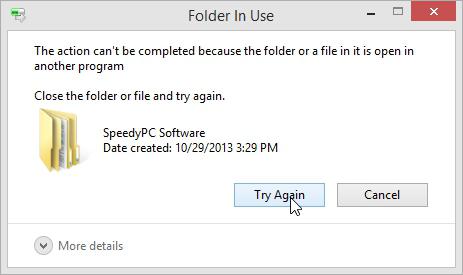
Sometimes the situation may be different. For example, an attempt to delete, rename, or move may fail when you are not logged on as an administrator, but on behalf of another user with limited rights. Probably, there is no need to explain that a file with system attributes cannot be deleted, as well as documents created using administrator rights in the main account. This is where the message "Could not find this item" pops up. How to delete such files, we will now figure it out.
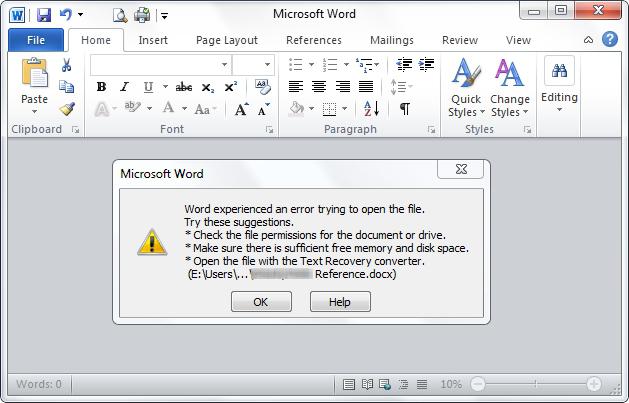
In addition, it is also worth noting that such errors can occur after renaming, say, office documents. Programs, as a rule, remember the last few files, so when using the quick opening of one of them, unpleasant situations can also arise when the application simply does not find the file you are looking for in the specified path.
The simplest way to fix a bug
First of all, every user should know that even having administrator rights is not always a guarantee of successful deletion, renaming or moving of locked files, since some files and folders of a system nature have long names. And only elements with short names that are usually inaccessible to the user are subject to deletion.
On the other hand, you can use the simplest method, which is to add some entries to the system registry. So, for example, the files FolderDescription-x86.reg (for 32-bit versions of Windows OS) and FolderDescription-x64.reg (for versions of Windows with 64-bit architecture) perfectly cope with such a problem. If there are no such files on the computer terminal (and this, as a rule, they are), they can be easily downloaded from the Internet. Don't worry, nothing terrible will happen, but you can be guaranteed to get rid of the "Unable to find this element" error. How to delete files after that? In the standard way. Only and everything.
Remains of "garbage" after uninstalling applications
In some cases, the error may appear when it is incomplete. It often happens that the “native” uninstaller of the program or the standard Windows InstallShield Wizard does not completely remove all components, prompting the user to delete some files manually. Very often this concerns the uninstall.exe uninstaller itself.
In this case, a message may also be displayed stating that the element was not found. correctly and completely, so that no unnecessary garbage remains in the system in the form of residual files or registry keys? It's very simple: it's better to use uninstallers like iObit Uninstaller, which remove absolutely all software components, as well as system registry entries and keys that cannot be removed by the usual method (Forced Uninstall).
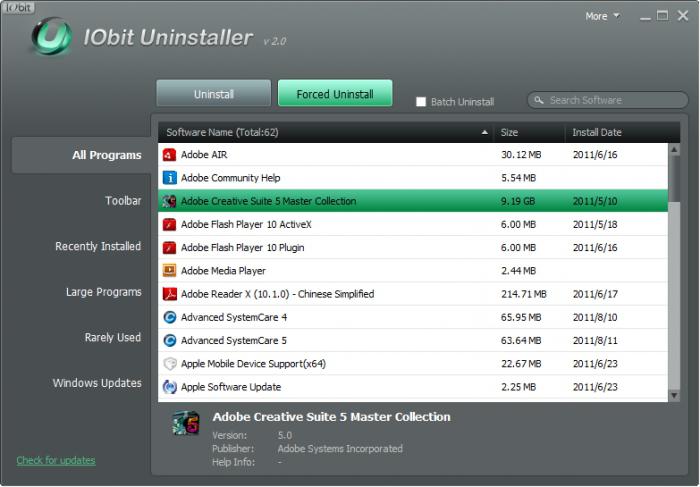
Yes, and rummaging through the registry in manual mode, too, do not want to. Moreover, this is undesirable.
Additional ways to remove stubborn files
Among the most common methods for deleting files and folders that cannot be deleted are the use of a special Unlocker utility, as well as direct deletion of elements with system attributes using a short name. In principle, both methods are good. However, the average user will have to tinker a bit with the names.
Program Unlocker
The Unlocker application is a universal option for solving many incidental situations. In fact, the program is a kind of means of unlocking access to any element of the system, after which it will be possible to perform the necessary actions.
As a rule, the program itself is already included in the Windows 7 OS. If it is not on the computer, it can be easily found and downloaded from the Internet.
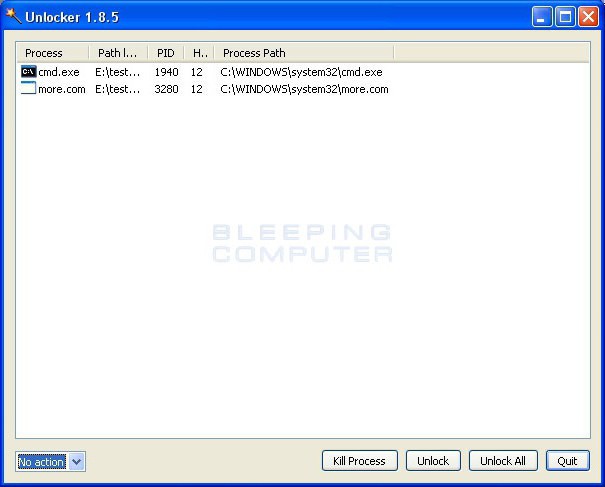
When you enter the same standard "Explorer" Windows, the corresponding command "Unlock all" will appear. The application will stop all processes associated with a particular file, after which it can be deleted or renamed without any problems. You can, of course, end related processes in the "Task Manager", but it's just not recommended to do this, because one process can be responsible for the operation of several programs and use many files (for example, dynamic libraries.dll). And the correct completion of the process in this case is not guaranteed.
Deleting files and folders with system names
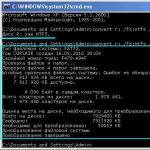
A slightly more complicated method, but no less effective, is to use short file and folder names. Suppose, during operations with a system file, an error occurs due to the fact that this element could not be found. How to remove it using this method, we will try to figure it out.
First of all, to uninstall, you will need to use either the Run menu. Let's say we have a file named "111" located in the Program Files folder on the C drive. The delete command will look like this: DEL \\.\C:\Program Files\111. For a folder named "111" located at the same address, the command takes the form RD \\.\C:\Program Files\111.
This method may not work when you need to know the short name of a file or folder. In this case, after starting the command line (cmd.exe), you must first execute the line CD drive letter:\path to file or folder\ /d, and then to get a short name - the DIR /X /N command. After the required name is known, the folder or file can be deleted as described above.