Mitsubishi Lancer IX has gained fame as a reliable and unpretentious car. Ideal things do not happen and the "Japanese" have their own weaknesses. Which each future owner should know about and which you should pay attention to when buying a used car of this model.
Weaknesses of the Mitsubishi Lancer of the 9th generation and their manifestations
- increased oil consumption;
- throttle assembly;
- brake discs and calipers;
- steering rack;
- catalytic converter;
- weak LCP.
The buyer of a used car should definitely pay attention to the following:
Increased oil consumption in cars with mileage of more than 100 thousand km.
This feature is “treated” by the correct selection of engine oil, and if it does not help, by replacing oil seals, oil scraper rings, which tend to sink and wear out, and repairing the engine, up to a major one;
Throttle assembly.
It “gnaws” a hole in the cylinder of the mechanism, at first this does not interfere, but it provokes increased wear of the mechanism. Also, washing the throttle assembly or an enlarged fossa leads to an increase in idle speed - up to 1500 - 2000 rpm. A common factory defect. It is solved by replacing the unit or repair according to the Titus method;
Brake discs and calipers.
The problem manifests itself when braking at high speeds. The steering wheel rattles, the brake discs heat up, they start to drive, warps. There were times when the knot was split in half. Disks need to be replaced, preferably with a high-quality non-original counterpart, and calipers are sorted out and worn parts change (cuffs, o-rings);
Steering rack
When driving in a straight line, knocks appear on small bumps, as if they knock on the steering column with a hammer. By 150 thousand run on every second car, this problem manifests itself. The main reason is the corrosion of the stem of the mechanism at the seal with the glands. Seals seals and oil leaks. This problem can be solved by buying a new rail (expensive pleasure), buying a used rail (analogy with the lottery: you can get into trouble-free and save money, or maybe leak again in a month), repair with replacing the stem and completely re-sorting and replacing all the oil seals. The output will be a practically new rail at a price 2-3 times cheaper. By the way, ships can also include weak tie rods;
Catalytic converter
There are two of them on Lancer. Due to the low quality of gasoline, it breaks down when it reaches 100 thousand, the first one, which is located on the exhaust manifold and works in more aggressive conditions. When the “Check Engine” lamp lights up and the reason is in the catalyst, there are not so many options, namely: replacing the converter (very expensive and inefficient, since gasoline again destroys it after 70 - 100 thousand), remove and fill it with a weak one (1 : 9) a solution of phosphoric acid and water. The method is not always effective and will help if the honeycomb is still in order. The third method consists of removing the catalyst and installing a snag for flashing the engine. Lambda probes that control the operation of the converter are moved to the second to “deceive” the engine control program;
Weak body paint.
Before buying a body inspection is required. Chips will subsequently lead to rust. Care with reconditioning polishes will help maintain coverage and extend its life.
In addition to the above-mentioned weak points of a car of this model, it is necessary to carefully inspect the entire car before buying. Unless of course there is no opportunity to drive her into a car service. It is worth a ride on it and listen to possible knocks, creaks, whistles, etc. In addition to the weaknesses of this car, there are a number of disadvantages that must be considered before buying a car.
Typical weaknesses of the Mitsubishi Lancer from 2007-2010. release
- very poor sound insulation;
- lack of illumination of the glove compartment (apparently the designer considered it unnecessary, even if they put the flashlight in the kit);
- inconvenient near / far switch;
- weak head optics;
- stiff suspension;
- expensive original spare parts, and by the way, by their durability, I would wish for the best;
- small amount of luggage;
- rattle of cheap plastic in the cabin;
- uncomfortable armrest;
- poor air conditioning and stove.
To summarize.
Despite the track record of weaknesses and weaknesses, the car is reliable, dynamic, especially with a two-liter engine, is well-controlled and looks good. When buying, the main thing is to carefully consider the inspection, and it is best to conduct diagnostics before buying, and also not to buy cars that were used in a taxi or in training novice drivers.
P.S: Dear owners of this car model, if, according to your observations during operation, frequently failing parts, assemblies or assemblies appear, we will be very grateful if you report these frequent breakdowns in the comments below!
Weaknesses and main weaknesses of the Mitsubishi Lancer IX was last modified: October 16, 2019 by Administrator
One of the urgent problems for owners of a beautiful car 🙂 from Mitsubishi is the diagnosis of Lancer 9. What if the check on Lancer 9 caught fire(check engine)? By the way, for those owners who do not know how to determine that the check has caught fire (and it is necessary to read the error codes), below is a photo of this situation.
So, to solve this problem, there are several ways diagnostics Lancer 9and to be precise - three. In this article we will talk about them.
Method One - Simple
The simplest and cheapest, but, unfortunately, does not allow to carry out diagnostics of Lancer 9. In this way, you can only reset the error (extinguish the check lamp). To do this, you need to remove the negative terminal from the battery for a while, after that the check lamp will go out - but you will not know the reason for the error. In this case, if there is a malfunction in the car, the check engine will light up again after a while.
Method Two - Car Service
Indeed, why not come to the car service for diagnostics Lancer 9? In this case, they will read the error to you and tell you the possible cause of the malfunction, and if possible (and if you have money), they will repair the car. But in this case there is one minus - the cost of diagnosis. Depending on the service, it ranges from 500 to 1000 rubles for reading codes and erasing errors. But, taking into account the “professionalism” of some service workers, the cause of the error cannot always be recognized correctly and the replacement of various units does not clean up the error (and the money has already been spent).
The third method is the best (according to the editors site)
Naturally, our article would be incomplete if we did not tell our readers about the third, rather simple and cheap way to diagnose Lancer 9. This method consists in purchasing the OBD2 ELM327 diagnostic adapter. This adapter allows you to read errors, diagnose a car by many parameters, as well as erase these errors. Let's talk about this adapter and how to use it for diagnostics Lancer 9 more details.
This adapter is currently available in three versions - Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and USB (shown below in the picture). These versions differ from each other only in how you will read and display the parameters of your car. The Bluetooth version is suitable for laptops with bluetooth, as well as for tablets and smartphones on android with bluetooth. The Wi-Fi version is also suitable for laptops with Wi-Fi and smartphones and tablets from Apple (i.e. for the iPhone and iPad). The USB version is suitable for laptops. Adapters also vary in size and color, but in terms of functionality they are the same.

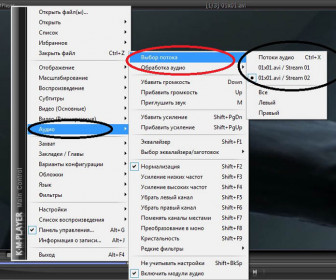
We will consider the operation of this adapter using the example of a Bluetooth adapter with an Android phone and Torque installed on it (you can download a diagnostic program for Lancer 9). For diagnostics, you must connect the adapter to the OBD2 connector on the Lancer (the black 16-pin connector is located under the plastic to the right of the steering wheel).


Next, using a smartphone in the bluetooth settings, we find the OBD2 adapter and connect to it (the password from the adapter is usually 1234, 7890 or 0000). Next, go to the Torque program, which itself will connect to the Lancer and begin to read the necessary parameters. Also in the program there is directly a menu item that responds to auto diagnostics and error reset (screenshots of the diagnostic program are presented below).

ATTENTION! The editors of the site advises you to remove the adapter at the end of the trip, because the power is always supplied to it, and it can drain the battery (with a long simple car).
How much does this adapter cost? - you ask. And almost nothing: 300-500 rubles in Chinese stores (bluetooth version). True, very often a marriage is sent when ordering - and it is a little expensive to send a defective item back to China. Therefore, you can buy this ELM327 OBD2 Bluetooth adapter in Russia - tested and guaranteed.
But, as you understand, reading errors is one thing, but decrypting error codes on Lancer 9- completely different. Especially for our readers below, we offer decoding of standard error codeson Lancer 9 and the POSSIBLE reasons for their appearance (note precisely the POSSIBLE).
Also, for visitors to our site, we suggest downloading error codes for Lancer 9.
Code No. P0105: Atmospheric Pressure Sensor Circuit
Atmospheric pressure sensor failure.
An open or short circuit in the atmospheric pressure sensor circuit or a poor contact in the connector.
.
Code No. P0110: Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Open or short circuit in the intake air temperature sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
<АКП>.
Code No. P0115: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Open or short circuit in the coolant temperature sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0120: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Throttle Position Sensor Failure.
Open or short circuit in the throttle position sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0125: Feedback Mode Setting Circuit (Oxygen Sensor)
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Damage to the wire harness in the oxygen sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
NOTE: When the front oxygen sensor is degraded, the voltage deviates from the nominal voltage (like the new sensor), equal to about 0.5 V with the stoichiometric composition of the working mixture. The consequences of this departure are corrected by the rear oxygen sensor. If the rear oxygen sensor does not respond well to changes in the composition of the working mixture due to its own degradation, it will not cope with the task of correcting the signals of the front sensor. Thus, even if the system enters the feedback control mode, the voltage amplitude at the front sensor decreases and does not reach 0.5 V. For this reason, DTC P0125 can be recorded.
Faulty exhaust system.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0130: Front Oxygen Sensor Circuit<датчик 1>
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Oxygen sensor failure.
Open or short circuit in the front oxygen sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0135: Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit<датчик 1>
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of the front oxygen sensor heater.
Open or short circuit in the front oxygen sensor heater circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0136: Rear Oxygen Sensor Circuit<датчик 2>
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of the rear oxygen sensor.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0141: Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit<датчик 2>
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of the rear oxygen sensor heater.
Open or short circuit in the rear oxygen sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0170: Fuel Supply System Malfunction
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Fuel supply system malfunction.
Failure of the front oxygen sensor.
Faulty intake air temperature sensor.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0201: Injector 1 Circuit
Code No. P0202: Injector 2 Chain
Code No. P0203: Injector 3 Chain
Code No. P0204: Injector 4 Chain
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Injector failure.
Open or short circuit in the injector circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0300: Registration of random misfires
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Crankshaft Position Sensor Failure
Incorrect composition of the working mixture.
Low compression.
Faulty coolant temperature sensor.
Timing belt slip.
Failure of the recirculation system and exhaust gas recirculation valve.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detector Circuit
Code No. P0302: Cylinder 2 Misfire Detector Circuit
Code No. P0303: Cylinder 3 Misfire Detector Circuit
Code No. P0304: Cylinder 4 Misfire Detector Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of one or more components of the ignition system.
Low compression.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0325: Knock Sensor Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Knock sensor failure.
Open or short circuit in the knock sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0335: Engine Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Faulty crankshaft position sensor.
Open or short circuit in the crankshaft sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0340: Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Camshaft position sensor failure.
Open or short circuit in the camshaft position sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0403: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid Valve Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of the electromagnetic (electrovacuum) EGR valve.
Open or short circuit in the circuit of the electric vacuum valve or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0421: Failure of the accelerated converter warm-up mode
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Catalytic converter degradation.
Failure of the front oxygen sensor.
Failure of the rear oxygen sensor.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0443: Absorber Purge Control Solenoid Valve Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of the absorber purge control solenoid valve.
Open or short circuit in the solenoid valve circuit or poor contact in the connector
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0500: Vehicle Speed \u200b\u200bSensor Circuit<МКП>
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Speed \u200b\u200bsensor failure.
Open or short circuit in the speed sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Code No. P0505: Idling Actuator Chain
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Open or short circuit in the drive circuit of the idle speed controller or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0513: Immobilizer Chain
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Open or short circuit in the immobilizer circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Immobilizer Failure.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0551: Fluid Pressure Sensor Circuit for Power Steering
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Failure of the pressure sensor in the power steering.
Open or short circuit in the pressure sensor circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P0622: Contact Generator Relay Contact Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
An open in the contact circuit of the excitation relay.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
Code No. P1603: Backup Circuit
POSSIBLE CAUSES OF FAULT
Open or short circuit in the backup circuit or poor contact in the connector.
Engine Control Block Failure<МКП>.
Engine / gearbox control unit failure<АКП>.
SRS Error Codes:
1A Front impact sensor (LH) short-circuited
1B Front impact sensor (LH) open-circuited
1C Front impact sensor (LH) short-circuited to power supply
1D Front impact sensor (LH) short-circuited to ground
2A Front impact sensor (RH) short-circuited
2B Front impact sensor (RH) open-circuited
2C Front impact sensor (RH) short-circuited to power supply
2D Front impact sensor (RH) short-circuited to ground
14 Analog G-sensor malfunction
15 Safing G-sensor short-circuited (for frontal collision)
16 Safing G-sensor open-circuited (for frontal collision)
21 * 3 Driver’s air bag squib short-circuited
22 * 3 Driver’s air bag squib open-circuited
24 * 3 Passenger’s (front) air bag squib short-circuited
25 * 3 Passenger’s (front) air bag squib open-circuited
26 * 3 Driver’s pre-tensioner squib short-circuited
27 * 3 Driver’s pre-tensioner squib open-circuited
28 * 3 Passenger’s (front) pre-tensioner squib short-circuited
29 * 3 Passenger’s (front) pre-tensioner squib open-circuited
31 SRS-ECU capacitor circuit voltage too high
32 SRS-ECU capacitor circuit voltage too low
34 * 2 SRS-ECU connector lock out of order
35 Ignition of the air bag completed
39 Air bag deployed simultaneously
41 * 2 Power supply voltage (IG1 (A) voltage) drops a0bnormally.
42 * 2 Power supply voltage (IG1 (voltage) drops abnormally.
43 * 2 SRS warning light circuit open-circuited
44 * 2 SRS warning light circuit malfunction
45 SRS-ECU non-volatile memory (EEPROM) and A / D converter system
46 * 2 Incorrect SRS-ECU
51 Driver’s air bag squib activating circuit short-circuited
52 Driver’s air bag squib activating circuit open-circuited
10.04.2014
I allow myself to be surprised at some of the messages on the Legion-Avtodat forum in the topic “Conference for auto-diagnostics on December 3-6 in Moscow”,
And I, for example, will always be grateful to the training courses with Sergei Pavlovich Gazetin. And I will always remember his words: “first of all, if you suspect“ mechanics ”, we connect the rarefaction sensor and look. If the vacuum is not normal, we are looking for mechanical problems ...rarefaction sensor - it's like a thermometer for a doctor". No, well, great said!
And when this Lancer came up for repairs with the problem of "stupid and does not go," then he did it right away:
· Recalled whether there was a similar problem on the same car? It was.
· Is everything ready to check the vacuum value? All is ready.
· Is there time “for thinking”? There is.
Let `s start?
A similar malfunction: “stupid and does not go” can occur for a variety of reasons. If you don’t have the experience of such repairs in your head and don’t know some of the basics, then it’s better not to undertake such repairs - you’ll scatter around and do nothing ...
Here can be tied and "mechanics", and the fuel system, and the ignition system. And even the “semi-wedge" of the wheel bearing (as an incredible option). Etc. When troubleshooting, it is important to correctly and accurately isolate the "weak link" and not be distracted by the unlikely.
It is not for nothing that the manufacturer writes in his manuals that "before making measurements and checks on a car, it is necessary to prepare it." Has anyone been surprised at this fact? Like, what to cook there, go ahead, check it out! But in vain, because it follows:
· Check that the temperature of the coolant is between 80-95 ° C. If there is no such temperature, you must start the engine and catch the temperature to the set temperature. Is someone not doing this? Well, do not do it ("to each his own"?), Then you will be surprised why the data taken is "somehow not like that." Everything is correct here, the manufacturer will not recommend the unnecessary!
· Turn off all consumers: stove, headlights, sidelights, radio and so on - nothing should be powered by a battery and affect the parameters of the information taken.
· Put the gearbox in the neutral position, if the gearbox is automatic, put the selector in the “P” mode (parking).
· Switch off the ignition, that is, put the ignition key in the “OFF” position.
Since I use the dealer scanner MUT3, then I do everything further - again, on the recommendation of the Manufacturer, the following:
· Disconnect the hose from the crankcase ventilation valve and connect the vacuum gauge
· I close the hole in the forced ventilation valve
· I start the engine, check the idle speed - they must be within the prescribed limits
I will focus on point two: “I close the hole in the forced ventilation valve”; Quite often, my colleagues called me, who read my articles and want to consult in something, and there were several questions that were answered after I asked again: “Was the hole in the PVC valve closed before the check?”
Well, there’s nothing wrong with that, everyone starts with something ... below is a screen from a scanner, look and analyze?

What can be read on the monitor of the scanner and what we take into work at the moment:
· Incorrect rarefaction readings (43 kPa)
· Parameters Long Trim and Short Trim “went negative”
Incorrect rarefaction readings (43 kPa)
Let's start with rarefaction, although this is not an exact definition. It’s more accurate to say “differential pressure”, since we are comparing the “barometric” (atmospheric) pressure ”and“ the real (actual) pressure in the intake manifold ”. The difference between them is called "rarefaction." In our case, the differential pressure \u003d 43 kPa. This alone begins to raise questions, since for such motors the value of DD (differential pressure) should be plus or minus 27-30 Kpa. The difference is palpable and there must be reasons for this.
Parameters Long Trim and Short Trim “went negative”
When these parameters go beyond the regulation (average value of about 0%) towards the enrichment or depletion of the fuel-air mixture, this can indicate any malfunction in the fuel system, in the intake-exhaust system, in the ignition system, etc. You can see my short video on the topic - “Before the replacement”
Here is the time to use a pressure sensor and really look at the processes taking place:

High-voltage pulse is highlighted in a red square on the waveform(I will call colloquially: "the moment of spark"). In the same place, in the red square there is the number "0", this is the top dead center. It turns out that the “spark is ignited” after passing the dead center. So it's time to look at the gas distribution system? Elegantly open and remove the casing ...
For clarity, the timing belt held a white stripe: "How is the mark." The white dot to the right and below is “as it should be.” In the lower right corner of the photo is a screen from the manual for this motor.

The installation mark has shifted and gone back. For what reason? There are no miracles, there is a reason for everything, and for this you need to go down the belt and inspect the shaft:

There is unusualness, there is “something” - but only a careful look will notice it. We look and study the question further:

Did you notice too? On the plane there is attrition. What can you say about this?
Well, in the meantime, you can watch another short video, everything becomes very clear there. Just indescribable beauty. And you can estimate how much the gear goes to the left and right and how this can affect the work of the gas distribution mechanism:
Conclusion after measurements: “replace gear”. After replacing the gear, the differential pressure readings leveled off and became satisfactory for stable motor operation:

And here is my third video - “After the replacement”:
But also on the crankshaft, you must pay attention. It is clear that “the iron is thick there - it will not be erased!”, But this trifle somehow annoys somehow ...
I will summarize a short result of the work done and draw my personal conclusions:
How wonderful this repair looks on paper! And not only this one - all articles on the "practice of repairs" - it is "easy, simple, beautiful." And if you think about it, ask the question: "Where does everything come from?" I think so: - If a person came to work in a car service, in diagnostics, then you must immediately discard the desire “Earn a lot! Now! Instantly!". For now, forget about it.
And to plunge headlong into study. You need to know so much that, as one friend of mine correctly said: “Damn, there are too few hours in a day!”
Why did I at the very beginning of my story mention about studying with S.P. Gazetin - this is a good way to expand the time frame of the day and in a few days to learn and study so many materials that it would take months or years for myself. All these “courses, conferences and similar events” are nothing but “squeeze”, as a concentrated thought, which the lecturer gives to the audience.
P.S While I was writing this article (and I wrote it for a long time, you understand that it’s not enough time), the Legion-Avtodata company announcedThe second conference "Auto repair technology. Diagnostics of modern power units" at the end of March 2014, - .
It was a good match. I looked at the conference program - interesting. Designed for a wide range of automotive professionals. But since I mainly deal with gasoline-powered cars Mitsubishi, Toyota, I chose the lecture of S.P. Gazetin for myself:"Diagnostics of gasoline engines according to the signals of oxygen sensors and the parameters of the lambda circuit using a scanner and an oscilloscope."
The following topics are very interesting for me from a practical point of view:
8. Fuel correction and fuel adaptation, parameters that describe the processes of fuel correction and adaptation, their interpretation (adaptive corrections, additive and multiplicative correction, possible options for displaying on the scanner display).
9. Use of fuel correction and adaptation parameters for diagnostics of the engine and its systems.
Book Mitsubishi Lancer 9 2003-2007 right-hand drive models gasoline, spare parts catalog. Guide to the repair and maintenance of the car. Legion Avtodata
mania for leaks of gasoline, oil, brake and coolant. Ensure the integrity of the wiring. Check the fit of the high voltage wires in the nests of the ignition coils and on the candles.
6. Turn on the ignition by turning the key in the ignition switch to the “ON” position. This will turn on the gasoline pump. Without closing the hood (in case of rain or snow, cover the hood), drive.
USEFUL TIPS
It is better to close the hood after the engine starts to work. Before this, it is advisable to inspect the engine again, to make sure that there are no leaks of fuel, oil, coolant, as well as extraneous sounds in its operation. If for any reason during an unsuccessful start attempt the spark plugs are “filled”, use the cylinder purge mode. To do this, press the accelerator pedal all the way and turn on the starter. In this mode, there is no fuel supply and excess gas is removed from the cylinders by a stream of fresh air, while the spark plugs are dried. After purging, try starting again as usual.
If the engine does not start, there are three main reasons:
The start system does not work;
The ignition system does not work;
The power system does not work.
Faults in the starter system
Faults in the start system are manifested in the abnormal operation of the starter. There are five main starter faults.
1. The starter does not turn on. The reason is a violation of contact connections, an open or short circuit in the starter switching circuits, a malfunction of the traction relay.
2. When the starter is turned on, multiple clicks are heard. The reason is a failure of the holding winding of the traction relay, the battery is very discharged, the contact connections in the starter circuit are loosened.
3. The starter turns on, but its anchor either does not rotate or rotates slowly. The reason is that the battery is discharged, contact connections are broken, the contacts of the traction relay are burned, the collector is dirty or the brushes are worn out, inter-turn or short circuit in the windings.
4. The starter turns on, its anchor rotates, but the flywheel remains motionless. The reason is the weakening of the fastening of the starter to the clutch housing, damage to the teeth of the flywheel or the drive gear, slipping of the freewheel of the drive, breakage of the lever, drive ring or buffer spring of the starter drive.
5. The starter does not turn off after starting the engine. The reason is a malfunction of the freewheel of the starter, sintering of the contacts of the traction relay. In case of such a malfunction, stop the engine immediately!
The indicated malfunctions require qualified intervention in a car service or upon arrival at the garage (see section 10 “Electrical equipment”, p. 184). Preliminarily, you can only check the degree of discharge of the battery with a voltmeter (for example, as part of an autotester) and the tightness of contact connections in the starter circuit.
Check
ignition systems
WARNING
Your vehicle has a high energy microprocessor ignition system (MPSZ). A voltage of approximately 40 000 V is applied to the high-voltage wires, and although it is not life-threatening at a low current value, a possible electric shock when checking the ignition system can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, if you take up the high-voltage wire with the ignition on, use a thick rubber glove or, in extreme cases, pliers with insulated handles.
USEFUL ADVICE
Before checking the ignition system, set the gearshift lever to the neutral position and leave the parking brake applied.

1. With the ignition switched off, check the integrity and fit of the high-voltage wires in the nests of the ignition coils.
2. Check the functioning of the ignition coils (see "", p. 200).

3. If the low-voltage circuit of the ignition coils is working, check for the presence of sparks on the spark plugs. Remove the high voltage wire from the spark plug of the 1st or 3rd cylinder. Insert a spare spark plug into the cable lug and press the metal part against the “mass” of the car (for example, to the engine intake pipe). Turn the crankshaft of the engine with a starter.
WARNINGS
Reliable contact of the spark plug body with the “mass” is required, since if an additional spark gap appears that is larger than the gap between the spark plug electrodes, damage to the high-voltage circuit of the ignition coil or engine control unit is possible. Conduct the specified test for no more than five seconds, so as not to damage the exhaust gas neutralizers when gasoline which is not burnt in the engine cylinders enters them.
4. If there is no spark, replace the high-voltage wires with new ones. You can pre-try to install new, but verified, "from a working machine."
5. If the spark does not appear after replacing the wires, replace the ignition coils (see "Removing, installing and checking the ignition coils", page 200). If there is a spark, but the engine does not start, replace the spark plugs with new ones. You can also pre-try to install new, but tested, "from a working machine."
6. If, after this, the engine does not start, check the engine control system for serviceability (see “Faults in the fuel injection system”, page 32).
Check engine power system
The main indicator of the health of the engine power system is the fuel pressure in the fuel rail. But first we recommend checking the condition of the air filter (see “Replacing the filter element of the air filter”, page 55), since this operation is simple and does not take much time. After you have verified that the air filter is clean, check the reliability of the electrical contacts in the wiring harness pads of the injection system components responsible for the fuel supply (electric fuel pump, injectors).
See also: